Large volumes of water are used in the textile industries for many purposes including washing, scouring, dyeing,printing, bleaching, and finishing cloth. These processes generate large amounts of waste water. Moreover, due to the increasing cost of wastewater treatment and stricter government regulations imposed on wastewater disposal, demands for new technologies have become more urgent to recycle the waste ( water and auxiliary chemicals) economically and ecologically. In addition, textile effluent contains valuable substances that can be recovered.
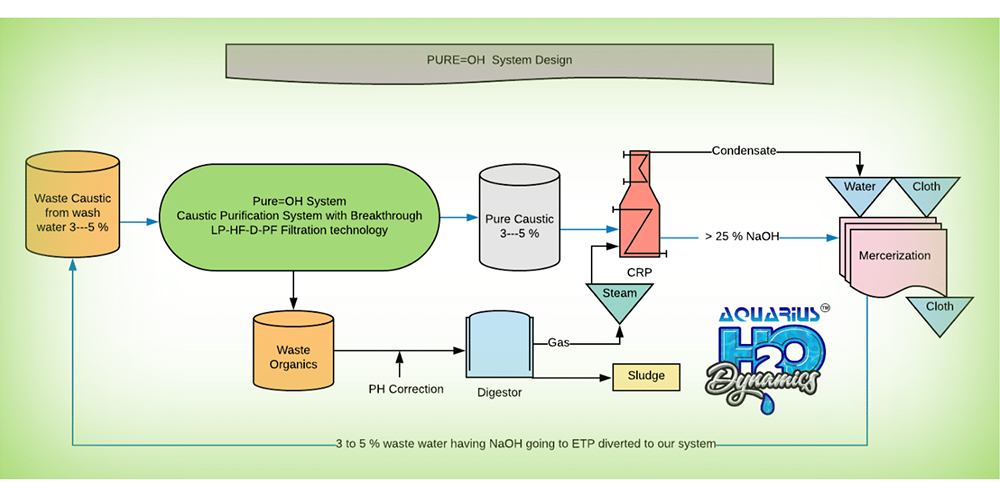
Caustic is used in the textile industry in two major applications : Purification of cellulosic fibers, to remove hemicellulose and other impurities from the fibers, to produce high purity cellulose, and higher quality dyeing and printing. The spent caustic, although still at high strength, cannot be reused in any of the plant operations due to the high concentration of contaminants. Hence, it is usually sent to the wastewater treatment plants, where in most causes it is neutralized with acid, increasing even more the costs of operation. Processing Units with Mercerization process had heavy load of NaOH as well as COD due to presence of starch in it increases TDS as well as COD at ETP