Greater attention and ongoing development work is happening in waste Water and particularly in MBRs. Hollow fiber , sheet and tubular are three types of configuration are available in market now a days. The process combines mixed liquor activated sludge, operating at high concentration, with ultrafilter membranes for biomass separation. Initially the process was limited to small wastewater flows where high quality treated effluent is required, due to high capital cost. With the awareness and ever increasing demands for higher effluent quality, MBRs are very much in demand and being applied in larger municipal sewage treatment plants as well as Industrial sectors now.
Tubular membranes configurations were developed in Netherlands, Germany and USA for use in MBRs and other processes respectively. The tubular membranes is most robust amongst other two membranes like hollow fiber and flat sheet membranes. Due to its life ,durability and economy it is being popular now a days and in much demand. BioLift ® MBR is placed outside tank so easy for maintenance. Longer life and easy maintenance had made tubular membranes as most desirable alternative.
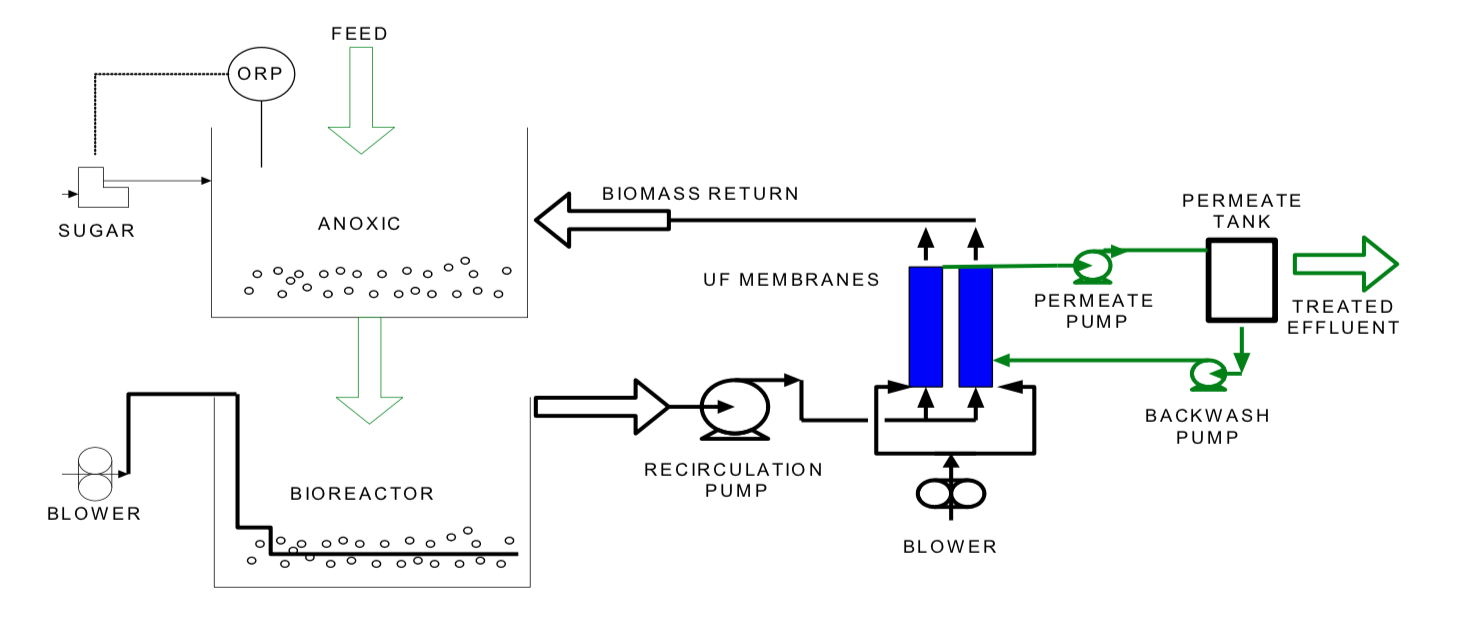
By placing the tubular modules vertically, and controlling the permeate extraction from membrane, it had proven that membrane flux is stable and fouling is less using less power. Air is injected at the bottom of the module , creating an airlift effect that increases the turbulence inside the tube and air bubbles travelling to top in tube had cleaning effect on inside the tube membranes wall . A periodic backwash of the membrane modules maintains consistent flux.
The flux is little less than standard cross flow configurations and power required is 10-20 % of Cross flow system. This power is very competitive with submerged product system. Low applied pressure and extremely low trans- membranes pressure (TMP) minimizes the amount and density of the solids boundary layer on the membrane surface. This produces very stable flux and low fouling rates
Flux Stability is enhanced by a periodic backwash. Cleaning is achieved by either injecting cleaning solutions with the backwash water, or by circulating or soaking cleaning solutions through the membrane modules. This effectively keeps the membrane flux at high levels.
The system operates on a continuous basis by controlling the rate of permeate flow from the membrane modules. A recirculation pump feeds mixed liquor from the bioreactor to the bottom of each module where air is injected. This, in effect, acts as an airlift pump increasing the velocity that aids scouring inside the membranes. The scouring mixers discharges from the top of each module and is returned to the bioreactor (or the anoxic zone for de-nitrification). Back-flushing with initiated on a time cycle to each bank of modules. This removes any cake formed on the inside of the membrane tubes, thus maintaining flux rates.